一、概念概述
-
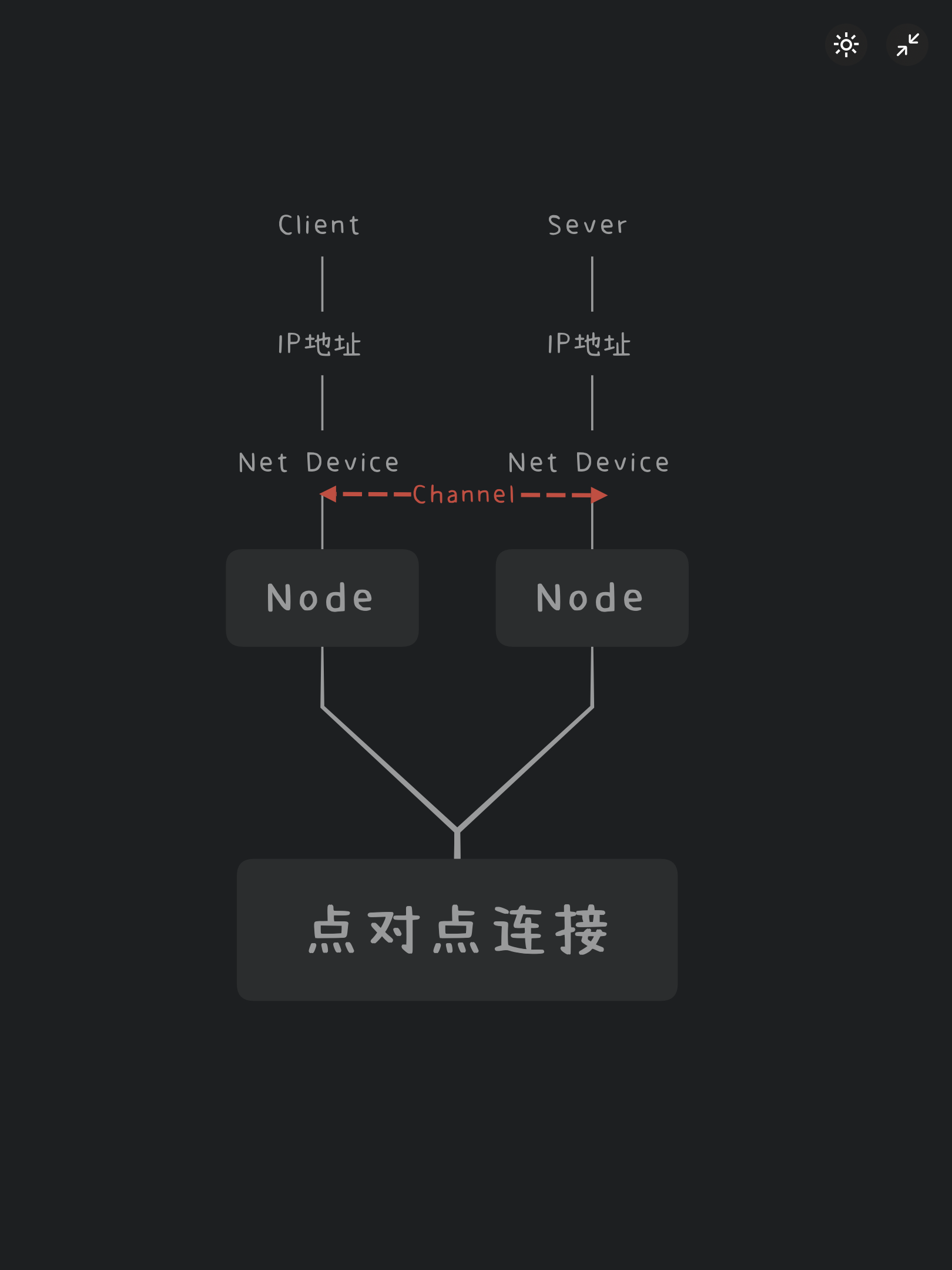
Node
互联网的终端系统或主机,相当于一台裸机,不过我们只需要添加其网络功能即可,不需要操作系统之类的。Node抽象由C++类表示,用于管理模拟中计算设备表示的方法。
-
Application
应用程序,用来生成一些模拟的活动,比如发送数据到另一台电脑。
-
Channel
信道,各个终端都是通过信道相互连接在一起,这里的信道可以是有线的(以太网),也可以是无线的(WiFi,蜂窝网络)。
-
Net Device
网络设备,相当于网卡一样的东西,只有安装在Node上,Node才可以进行网络通信。
-
Topology Helpers
用于帮助构建Node、Channel、Net Device等类,当网络结构比较庞大复杂时,用拓扑帮助可以更快的构建这些基类。
二、第一个例子代码解读
简单实现两个终端系统的网络互连
#include "ns3/core-module.h"
#include "ns3/network-module.h"
#include "ns3/internet-module.h"
#include "ns3/point-to-point-module.h"
#include "ns3/applications-module.h"
//"ns3/core-module.h"是ns3的核心模块需要的;
//"ns3/network-module.h"是ns3的网络模块;
//"ns3/applications-module.h"是ns3的应用模块需要的;
//一般我们自己写脚本时,上面三个都是必要的。
//"ns3/internet-module.h"是ns3提供的因特网模块需要的;
//"ns3/point-to-point-module.h"是点对点通信模块需要的。
// Default Network Topology
//
// 10.1.1.0
// n0 -------------- n1
// point-to-point
//
using namespace ns3;
NS_LOG_COMPONENT_DEFINE ("FirstScriptExample");
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
//接收命令行参数
CommandLine cmd (__FILE__);
cmd.Parse (argc, argv);
//设置时间分辨率为1纳秒
Time::SetResolution (Time::NS);
//启用 Echo 客户端和 Echo 服务器应用程序中内置的两个日志记录组件
LogComponentEnable ("UdpEchoClientApplication", LOG_LEVEL_INFO);
LogComponentEnable ("UdpEchoServerApplication", LOG_LEVEL_INFO);
//创建 ns-3 对象,这些对象将表示模拟中的计算机
//NodeContainer,Node容器,同于存放node,方便管理和使用
NodeContainer nodes;
nodes.Create (2);
//使用点到点拓扑助手类帮助我们直接设置NetDevice和Channel,相当于现实世界的网卡和信道
PointToPointHelper pointToPoint;
//网卡速率为5Mbps
pointToPoint.SetDeviceAttribute ("DataRate", StringValue ("5Mbps"));
//信道延迟为2ms
pointToPoint.SetChannelAttribute ("Delay", StringValue ("2ms"));
//NetDevice容器
NetDeviceContainer devices;
//在内部,创建一个NetDeviceContainer。对于NodeContainer中的每个节点(点对点链接必须正好有两个节点) ,将创建一个PointToPointNetDevice并将其保存在设备容器中。创建PointToPointChannel并附加两个PointToPointNetDevice。当PointToPointHelper创建对象时,以前在助手中设置的Attritribute用于初始化创建对象中的相应Attritribute。
//拓扑助手将Channel与NetDevice 安装到节点上----重要的一步
devices = pointToPoint.Install (nodes);
//这一步之后,每个节点都会有点对点网络设备(网卡)和它们之间的单个点对点通道
//节点上有了设备,开始安装协议
//网络堆栈助手相当于点对点助手,只不过它是帮助节点安装网络协议堆栈(TCP、UDP、IP)
InternetStackHelper stack;
stack.Install (nodes);
//为每个网络设备配置ip地址
Ipv4AddressHelper address;
//设置基础ip地址和网络掩码
address.SetBase ("10.1.1.0", "255.255.255.0");
//我们使用 IPv4Interface 对象在 IP 地址和设备之间建立关联。
Ipv4InterfaceContainer interfaces = address.Assign (devices);
//现在我们有了点对点网络,并有了网络协议和ip地址,接下来需要应用程序产生流量。
//设置服务端应用程序
UdpEchoServerHelper echoServer (9);
ApplicationContainer serverApps = echoServer.Install (nodes.Get (1));
serverApps.Start (Seconds (1.0));
serverApps.Stop (Seconds (10.0));
//设置客户端应用程序
UdpEchoClientHelper echoClient (interfaces.GetAddress (1), 9);
echoClient.SetAttribute ("MaxPackets", UintegerValue (1));
echoClient.SetAttribute ("Interval", TimeValue (Seconds (1.0)));
echoClient.SetAttribute ("PacketSize", UintegerValue (1024));
ApplicationContainer clientApps = echoClient.Install (nodes.Get (0));
clientApps.Start (Seconds (2.0));
clientApps.Stop (Seconds (10.0));
//运行
Simulator::Run ();
Simulator::Destroy ();
return 0;
}
下图是该实例的简单拓扑图
三、Logging日志模块
日志七个等级:
| 日志级别 | 日志描述(关联的宏:) |
|---|---|
| LOG_ERROR | 记录错误消息(关联的宏:NS_LOG_ERROR) |
| LOG_WARN | 日志警告消息(关联的宏:NS_LOG_WARN) |
| LOG_DEBUG | 记录相对罕见的临时调试消息(关联的宏:NS_LOG_DEBUG) |
| LOG_INFO | 记录有关程序进度的信息性消息(关联的宏:NS_LOG_INFO) |
| LOG_FUNCTION | 记录描述每个调用的函数的消息(两个关联的宏:NS_LOG_FUNCTION,用于成员函数,NS_LOG_FUNCTION_NOARGS,用于静态函数) |
| LOG_LOGIC | 描述函数内逻辑流的日志消息(关联的宏:NS_LOG_LOGIC) |
| LOG_ALL | 记录上面提到的所有内容(没有关联的宏) |
I、通过设置shell环境变量
1.调整日志等级
$ export NS_LOG=UdpEchoClientApplication=level_all
需要注意的是 NS_LOG后的日志模块必须已经被定义过,要么自己定义,要么导入包中已经存在,UdpEchoClientApplication就是包中内置的日志模块
上面这行命令执行完后,用export -p可以看到以下信息:
$ export -p
declare -x NS_LOG="UdpEchoClientApplication=level_all"
环境变量的NS_LOG就发生了改变,然后运行脚本发现打印出来的东西变多了
#没有设置环境变量之前的输出
At time +2s client sent 1024 bytes to 10.1.1.2 port 9
At time +2.00369s server received 1024 bytes from 10.1.1.1 port 49153
At time +2.00369s server sent 1024 bytes to 10.1.1.1 port 49153
At time +2.00737s client received 1024 bytes from 10.1.1.2 port 9
#设置完环境变量的输出,可以看到只多了客户端应用程序的一些信息,服务端并没有增加,因为我们只把客户端的日志等级调到了最高级
UdpEchoClientApplication:UdpEchoClient(0xef90d0)
UdpEchoClientApplication:SetDataSize(0xef90d0, 1024)
UdpEchoClientApplication:StartApplication(0xef90d0)
UdpEchoClientApplication:ScheduleTransmit(0xef90d0, +0ns)
UdpEchoClientApplication:Send(0xef90d0)
At time +2s client sent 1024 bytes to 10.1.1.2 port 9
At time +2.00369s server received 1024 bytes from 10.1.1.1 port 49153
At time +2.00369s server sent 1024 bytes to 10.1.1.1 port 49153
UdpEchoClientApplication:HandleRead(0xef90d0, 0xee7b20)
At time +2.00737s client received 1024 bytes from 10.1.1.2 port 9
UdpEchoClientApplication:StopApplication(0xef90d0)
UdpEchoClientApplication:DoDispose(0xef90d0)
UdpEchoClientApplication:~UdpEchoClient(0xef90d0)
2.确定哪个方法生成的日志信息——prefix_func
$ export 'NS_LOG=UdpEchoClientApplication=level_all|prefix_func'
UdpEchoClientApplication:UdpEchoClient(0xea8e50)
UdpEchoClientApplication:SetDataSize(0xea8e50, 1024)
UdpEchoClientApplication:StartApplication(0xea8e50)
UdpEchoClientApplication:ScheduleTransmit(0xea8e50, +0ns)
UdpEchoClientApplication:Send(0xea8e50)
###
#只有客户端的前面打印出了方法,想要服务端打印出来方法,操作和客户端一样
UdpEchoClientApplication:Send(): At time +2s client sent 1024 bytes to 10.1.1.2 port 9
At time +2.00369s server received 1024 bytes from 10.1.1.1 port 49153
At time +2.00369s server sent 1024 bytes to 10.1.1.1 port 49153
UdpEchoClientApplication:HandleRead(0xea8e50, 0xea5b20)
UdpEchoClientApplication:HandleRead(): At time +2.00737s client received 1024 bytes from 10.1.1.2 port 9
###
UdpEchoClientApplication:StopApplication(0xea8e50)
UdpEchoClientApplication:DoDispose(0xea8e50)
UdpEchoClientApplication:~UdpEchoClient(0xea8e50)
$ export 'NS_LOG=UdpEchoClientApplication=level_all|prefix_func:UdpEchoServerApplication=level_all|prefix_func'
这行命令使得客户端。服务端日志等级都为最高级,且前面加上方法调用,输出就不展示了。
3.查看日志生成的模拟时间——prefix_time
$ export 'NS_LOG=UdpEchoClientApplication=level_all|prefix_func|prefix_time:UdpEchoServerApplication=level_all|prefix_func|prefix_time'
II、通过宏来定义、开启、显示日志信息
1.宏定义日志信息
NS_LOG_COMPONENT_DEFINE ("FirstScriptExample");
定义了本文件的日志模块
2.宏开启日志信息,并设置日志等级——LogComponentEnable(name, level)
LogComponentEnable ("FirstScriptExample", LOG_LEVEL_INFO);
等价于shell中:export NS_LOG = ‘FirstScriptExample=info’
例如第一个例子中的这两行,这是内置的日志模块
LogComponentEnable ("UdpEchoClientApplication", LOG_LEVEL_INFO); LogComponentEnable ("UdpEchoServerApplication", LOG_LEVEL_INFO);开启它们只能显示对应模块它们自己的日志信息,并不能显示自己写的文件的日志信息
3.输出日志信息
以下三行代码,要根据我们开启的日志等级进行输出
NS_LOG_WARN("Message:level_warn");
NS_LOG_INFO("Message:level_info");
NS_LOG_LOGIC("Message:level_logic");
因为开启的级别是info,所以只有Message:level_warn和Message:level_info会被输出。
想要在该文件下打印日志信息,必须定义开启同名的日志,如上面提到的FirstScriptExample,若只定义不开启,则三行代码都不会输出,只开启不定义必然报错;UdpEchoClientApplication与UdpEchoServerApplication的日志模块是内置的,不是该文件下的,所以开启了也无法输出该文件下的日志信息
四、命令行参数
使用命令行参数系统的第一步是声明命令行解析器
int
main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
...
CommandLine cmd;
cmd.Parse (argc, argv);
...
}
在命令行里打印有关信息
$ ./ns3 run "scratch/myfirst --PrintHelp"
#打印出的信息
General Arguments:
--PrintGlobals: Print the list of globals.
--PrintGroups: Print the list of groups.
--PrintGroup=[group]: Print all TypeIds of group.
--PrintTypeIds: Print all TypeIds.
--PrintAttributes=[typeid]: Print all attributes of typeid.
--PrintVersion: Print the ns-3 version.
--PrintHelp: Print this help message.
$ ./ns3 run "scratch/myfirst --PrintAttributes=ns3::PointToPointNetDevice"
#打印信息中的一条
--ns3::PointToPointNetDevice::DataRate=[32768bps]:
The default data rate for point to point links
可以看到默认网络设备的DataRate是32768bps,而我们在程序中设置的是5Mbps将默认值覆盖掉了,如果把程序中的5Mbps注释掉,打印结果如下
PointToPointHelper pointToPoint;
//pointToPoint.SetDeviceAttribute ("DataRate", StringValue ("5Mbps"));
$ export 'NS_LOG=UdpEchoServerApplication=level_all|prefix_time'
+0.000000000s UdpEchoServerApplication:UdpEchoServer(0x20d0d10)
+1.000000000s UdpEchoServerApplication:StartApplication(0x20d0d10)
At time +2s client sent 1024 bytes to 10.1.1.2 port 9
+2.257324218s UdpEchoServerApplication:HandleRead(0x20d0d10, 0x20900b0)
+2.257324218s At time +2.25732s server received 1024 bytes from 10.1.1.1 port 49153
+2.257324218s Echoing packet
+2.257324218s At time +2.25732s server sent 1024 bytes to 10.1.1.1 port 49153
At time +2.51465s client received 1024 bytes from 10.1.1.2 port 9
+10.000000000s UdpEchoServerApplication:StopApplication(0x20d0d10)
UdpEchoServerApplication:DoDispose(0x20d0d10)
UdpEchoServerApplication:~UdpEchoServer(0x20d0d10)
现在,它在 2.25732 秒处接收数据包。这是因为我们刚刚将的数据速率从每秒5兆位降至默认的每秒32768位。
通道延迟也是同样的道理,这里只放一下延迟的默认值
$ ./ns3 run "scratch/myfirst --PrintAttributes=ns3::PointToPointChannel"
--ns3::PointToPointChannel::Delay=[0ns]:
Transmission delay through the channel
最后,只需要在命令行里给注释掉的DataRate与Delay属性赋值,就可以和源代码输出同样的结果
$ ./ns3 run "scratch/myfirst --ns3::PointToPointNetDevice::DataRate=5Mbps --ns3::PointToPointChannel::Delay=2ms"
也可以将自己的钩子函数添加到命令行系统
int
main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
uint32_t nPackets = 1;
CommandLine cmd;
cmd.AddValue("nPackets", "Number of packets to echo", nPackets);
cmd.Parse (argc, argv);
...
echoClient.SetAttribute ("MaxPackets", UintegerValue (nPackets));
...
命令行里输入MaxPackets的值
$ ./ns3 run "scratch/myfirst --nPackets=2"
成功看到两个数据包的回显
+0.000000000s UdpEchoServerApplication:UdpEchoServer(0x836e50)
+1.000000000s UdpEchoServerApplication:StartApplication(0x836e50)
At time +2s client sent 1024 bytes to 10.1.1.2 port 9
+2.003686400s UdpEchoServerApplication:HandleRead(0x836e50, 0x8450c0)
+2.003686400s At time +2.00369s server received 1024 bytes from 10.1.1.1 port 49153
+2.003686400s Echoing packet
+2.003686400s At time +2.00369s server sent 1024 bytes to 10.1.1.1 port 49153
At time +2.00737s client received 1024 bytes from 10.1.1.2 port 9
At time +3s client sent 1024 bytes to 10.1.1.2 port 9
+3.003686400s UdpEchoServerApplication:HandleRead(0x836e50, 0x8450c0)
+3.003686400s At time +3.00369s server received 1024 bytes from 10.1.1.1 port 49153
+3.003686400s Echoing packet
+3.003686400s At time +3.00369s server sent 1024 bytes to 10.1.1.1 port 49153
At time +3.00737s client received 1024 bytes from 10.1.1.2 port 9
+10.000000000s UdpEchoServerApplication:StopApplication(0x836e50)
UdpEchoServerApplication:DoDispose(0x836e50)
UdpEchoServerApplication:~UdpEchoServer(0x836e50)
五、跟踪系统
I、Ascii跟踪
在Simulator::Run ()之前添加两行代码,开启Ascii跟踪
AsciiTraceHelper ascii;
pointToPoint.EnableAsciiAll (ascii.CreateFileStream ("myfirst.tr"));
写在PointToPointHelper定义之后并没有生效,
PointToPointHelper pointToPoint; AsciiTraceHelper ascii; pointToPoint.EnableAsciiAll (ascii.CreateFileStream ("myfirst.tr"));而在Run之前生效了
AsciiTraceHelper ascii; pointToPoint.EnableAsciiAll (ascii.CreateFileStream ("myfirst.tr")); Simulator::Run ();
在本例中,我们将跟踪模拟中每个点对点网络设备中存在的传输队列上的事件。传输队列是一个队列,发往点对点通道的每个数据包都必须通过该队列。请注意,跟踪文件中的每一行都以一个单独字符开头(后面有一个空格)。此字符将具有以下含义:
+:设备队列上发生排队操作;-:设备队列上发生取消排队操作;d:数据包被丢弃,通常是因为队列已满;r:网络设备收到数据包。
II、pcap 跟踪
启用代码
pointToPoint.EnablePcapAll ("myfirst");
结果查看
$ tcpdump -nn -tt -r myfirst-0-0.pcap
reading from file myfirst-0-0.pcap, link-type PPP (PPP)
2.000000 IP 10.1.1.1.49153 > 10.1.1.2.9: UDP, length 1024
2.514648 IP 10.1.1.2.9 > 10.1.1.1.49153: UDP, length 1024
tcpdump -nn -tt -r myfirst-1-0.pcap
reading from file myfirst-1-0.pcap, link-type PPP (PPP)
2.257324 IP 10.1.1.1.49153 > 10.1.1.2.9: UDP, length 1024
2.257324 IP 10.1.1.2.9 > 10.1.1.1.49153: UDP, length 1024
vim不能查看pcap文件,只能用tcpdump读取